Heat pumps are transforming the way modern homes are heated and cooled, bringing both efficiency and environmental mindfulness into every room. Unlike traditional methods that rely on combustion, heat pumps offer a sustainable solution that benefits homeowners and the planet. Interested in expert installation? Explore your options with a family-owned heat pump service for guidance and support tailored to your needs.
As homeowners continue to prioritize comfort and energy savings, heat pumps have seen a rise in demand due to their reliability, versatility, and ability to address both winter and summer climate control needs with a single system. This technology fits seamlessly into the evolving landscape of residential heating and cooling, delivering robust results in diverse environments. With clear advantages over older HVAC technology, heat pumps support modern living while also aligning with eco-friendly priorities.
Table of Contents
How Heat Pumps Work
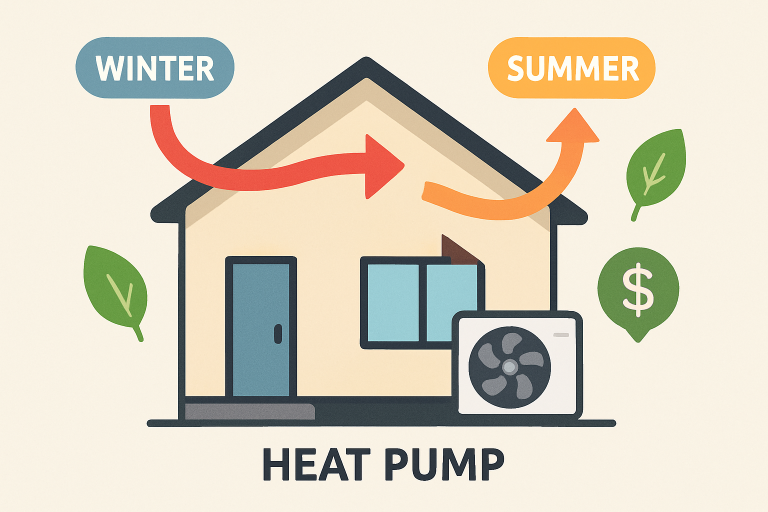
Heat pumps function by shifting heat rather than generating it—taking advantage of temperature differences between indoors and outdoors. During colder months, they extract ambient heat from the air, ground, or nearby water sources, delivering it indoors where it’s needed. On hotter days, the process is reversed, allowing excess indoor heat to be expelled outside, much like an air conditioner, but with far greater efficiency. This efficient heat transfer process is the cornerstone of their lower energy use when compared to traditional systems, as detailed by sources such as the U.S. Department of Energy.
Types of Heat Pumps
The right heat pump technology depends on climate, building design, and available natural resources. Understanding the main types can help you choose the most suitable solution for your household:
- Air-Source Heat Pumps (ASHPs): Capturing energy from outside air, these are the most common and cost-effective choice in milder climates.
- Ground-Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs): Also known as geothermal pumps, these systems tap into the earth’s stable underground temperature through buried loops, making them well-suited for areas with extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Water-Source Heat Pumps: Drawing heat from nearby lakes, ponds, or rivers, these are ideal in locations with accessible water features and are prized for their high efficiency when water is available year-round.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Heat pumps are engineered to provide significant cost savings on energy bills. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), homeowners who switch to heat pumps can see reductions in annual utility costs by $300 to $650, depending on their system’s efficiency and local utility rates. The high performance of heat pumps stems from their ability to transfer heat, rather than produce it, resulting in three to four times more heating and cooling output for the same energy input compared to electric resistance heaters or furnaces.
Environmental Impact
Heat pumps substantially lower a home’s carbon footprint. By leveraging existing natural energy sources and using electricity more efficiently, they reduce the need for fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recognizes ground-source heat pumps, particularly as one of the cleanest heating and cooling options available today. By using and promoting these systems, homeowners play an active role in reducing climate change and advancing local sustainability goals.
Installation Considerations
Proper planning is vital for the optimal performance of any heat pump system. Key considerations include:
- Climate Suitability: Select a type designed for your geographic region—air-source models perform best in moderate areas, while ground or water-source models can handle more extreme climates.
- Home Insulation: Efficient heat pumps require strong insulation to maximize benefits; upgrading your insulation may be recommended as part of your installation.
- Space Requirements: Ground-source systems need outdoor space for loops and trenches, while air-source models require adequate clearance for airflow around units.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Financial support is available for homeowners who install heat pumps, making the initial investment more accessible. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act offers a federal tax credit of up to 30% of the cost for qualifying systems, and local incentive programs, such as those in San Francisco, provide additional rebates or bill credits. For instance, the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission offers a $100 rebate for the purchase and installation of a hot water recirculation pump, which can complement your heat pump system. Additionally, programs like BayREN’s Single Family Home+ offer rebates for heat pump installations, though these are subject to change and should be verified for current availability. These measures make upgrading to energy-efficient systems both practical and affordable for a broad range of households.
Maintenance and Longevity
With simple, regular upkeep, heat pumps deliver dependable service and significant energy savings for many years. Vital maintenance steps include:
- Changing or cleaning air filters monthly to maintain airflow and efficiency.
- Annual inspections and cleaning of coils, fans, and compressor systems.
- Clearing debris and obstructions from around outdoor units to ensure unhindered operation.
Most heat pumps last between 15 and 20 years, making them a smart, long-term investment in comfort and sustainability.
Final Thoughts
For homeowners seeking an energy-smart, environmentally conscious way to keep their homes comfortable year-round, heat pumps are the solution of the future. With an array of types to suit diverse climates and new construction or retrofit scenarios, these systems offer clear economic and ecological benefits. Consider your home’s needs and the available incentives to make a decision that advances both your comfort and your commitment to sustainable living.