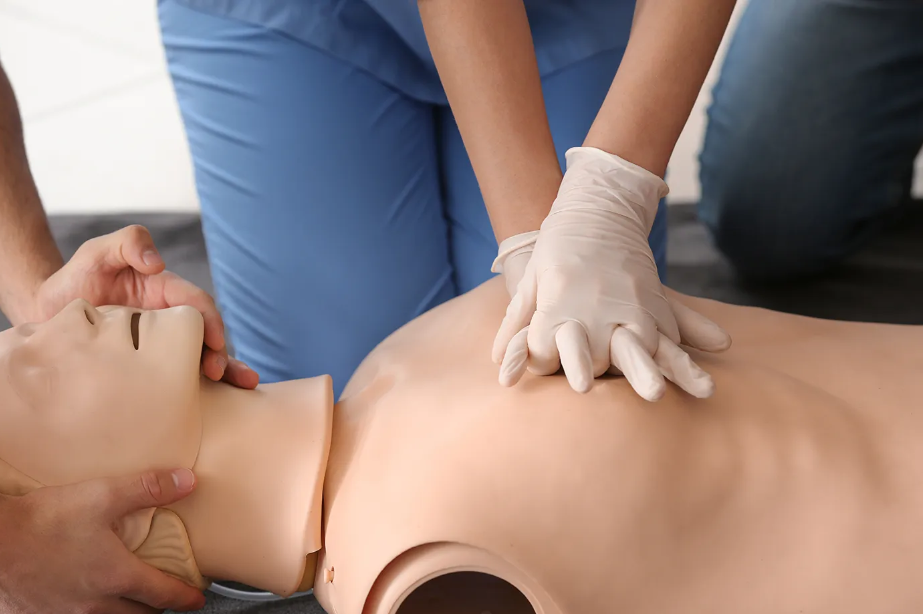
In moments of medical emergency, understanding the nuances of life-saving techniques can mean the difference between life and death. Among the fundamental tools in emergency response are Basic Life Support (BLS) and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). These techniques serve as vital pillars in the chain of survival, offering critical interventions to individuals in distress. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the essentials of BLS and CPR, understand their differences, and navigate their roles in emergency care.
Table of Contents
Understanding BLS and CPR:
Basic Life Support (BLS) and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) are crucial techniques used to sustain life in emergencies, particularly when someone’s heart has stopped beating or breathing.
BLS encompasses a broader spectrum of life-saving interventions beyond CPR alone. It includes assessing the patient’s condition, activating emergency medical services (EMS), performing high-quality chest compressions, providing rescue breaths, and utilizing automated external defibrillators (AEDs) when available. BLS training often targets healthcare professionals and first responders who may encounter cardiac arrest or other life-threatening emergencies.
On the other hand, CPR specifically refers to the manual technique of providing chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood circulation and oxygenation in someone who is in cardiac arrest or experiencing respiratory failure. CPR is a critical intervention that can be performed by trained individuals of all backgrounds, including healthcare providers, lay rescuers, and members of the public.
Distinguishing Between BLS and CPR:
While BLS and CPR share the common goal of preserving life in emergency situations, they differ in scope and complexity.
BLS encompasses a more comprehensive set of skills and interventions, including the initial assessment of the patient’s condition, activation of EMS, use of AEDs, and advanced airway management techniques such as bag-valve-mask ventilation. BLS training emphasizes the importance of early recognition and prompt intervention in cardiac emergencies, aiming to optimize outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
On the other hand, CPR focuses specifically on the performance of chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood flow and oxygenation in the absence of a pulse or effective breathing. CPR training emphasizes the importance of providing high-quality compressions at the correct depth and rate and delivering effective rescue breaths to maximize oxygen delivery to the lungs.
In emergency care settings, both BLS and CPR play critical roles in the continuum of care for patients in cardiac arrest or respiratory distress. Healthcare providers are trained to assess the patient’s condition, initiate BLS interventions as needed, and provide advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) interventions such as medications and advanced airway management.
For lay rescuers and members of the public, CPR training equips individuals with the skills and confidence to intervene effectively in emergency situations outside of healthcare settings. By performing CPR promptly and effectively, lay rescuers can buy valuable time for the patient until EMS arrives, significantly improving the chances of survival.
The Importance of BLS vs CPR:
BLS and CPR are indispensable elements of emergency response, each playing a distinct yet complementary role in preserving life. While BLS encompasses a broader array of interventions, including the utilization of AEDs and advanced airway management, CPR specifically concentrates on executing chest compressions and rescue breaths to uphold blood circulation and oxygenation.
When navigating the intricacies of emergency care, it’s vital to discern the distinct contributions of BLS vs CPR and discern when to employ each intervention. By mastering both BLS and CPR techniques, individuals can emerge as adept first responders capable of effecting change in life-threatening situations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, BLS and CPR are essential life support techniques that play critical roles in emergency care. While BLS encompasses a broader spectrum of interventions, CPR specifically focuses on maintaining blood circulation and oxygenation in cardiac arrest or respiratory failure. By understanding the distinctions between BLS and CPR and mastering their respective techniques, individuals can become effective first responders capable of navigating life-saving interventions in times of crisis.
Whether you’re a healthcare provider, first responder, or lay rescuer, proficiency in BLS and CPR is an invaluable asset that can make a significant difference in the outcome of medical emergencies. By prioritizing training and education in BLS and CPR, individuals can empower themselves to be prepared and confident in their ability to respond effectively when seconds count.

